Emerging cyber threats pose significant risks to network security, making it essential for organizations to adopt robust security measures. The rapid evolution of cyber-attacks demands a proactive approach to securing and managing networks. This article provides comprehensive guidance on how to effectively counter these evolving threats, offering insights into various aspects of network security.
Identifying and Managing Network Assets
Importance of Asset Identification
Understanding the importance of asset identification is crucial in various fields, including finance, logistics, and information technology. Accurate identification of assets ensures efficient tracking, management, and utilization of resources, thereby enhancing operational effectiveness and financial performance.
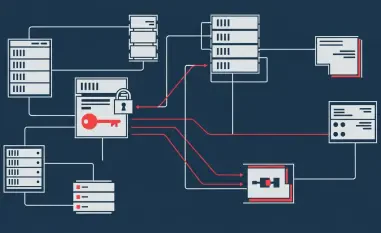
Before strides can be made in securing a network, a crucial first step involves identifying and cataloging all network assets. Far too often, organizations find themselves vulnerable because they overlook unsecured or improperly decommissioned systems that become gateway points for attackers. A complete and thorough knowledge of all devices, software, and other components that join your network infrastructure is fundamental to understanding your threat landscape. This vital process not only helps in recognizing potential weak points but also lays the foundation for targeted security strategies that mitigate unforeseen risks.
The failure to continually monitor and update your list of assets can lead to significant vulnerabilities. For instance, old devices that haven’t been updated with the latest security patches may become easy prey for cybercriminals. Similarly, not decommissioning unused or outdated systems could leave backdoors open for potential breaches. By consistently managing and tracking all elements within your network, you enhance your ability to protect the organization comprehensively.
Asset Management Practices
Adopting a systematic approach to asset management ensures that organizations are always aware of their network’s components. This involves maintaining an updated inventory of devices and continuously monitoring their state of security. Such a systematic process can include several best practices like regular audits, real-time state monitoring, and automated alerts for non-compliant or unknown devices. Automation can significantly reduce manual effort, ensuring that new devices are immediately recognized and assessed based on the organization’s security policies.
Interestingly, effective asset management also covers the end-of-life phase of gadgets and systems. Properly decommissioning and securely disposing of outdated equipment mitigates the risks associated with residual data leaks or unauthorized access. By ensuring that devices are completely wiped and their data securely erased before disposal, organizations can prevent data from falling into the wrong hands. These measures form a sustainable cycle of security hygiene that proactively defends against emerging cyber threats.
Understanding and Modeling Threats
Role of Threat Modeling
Furthering network security necessitates a deep understanding of the specific threats that may target your organization. Here, threat modeling becomes an invaluable tool, allowing organizations to predict potential attack vectors based on past trends and current vulnerabilities. Threat modeling involves identifying the assets at risk, the potential threat actors, and how these threats could manifest into real-world attacks. By aligning security controls precisely with these predicted threats, organizations can avoid the trap of spending valuable resources on negligible risks while ignoring more severe vulnerabilities.
Investment in threat modeling not only sharpens focus on probable attack methods but also fosters a proactive security culture. Rather than reacting to threats, firms can anticipate them, thereby reducing the window of vulnerability. The precision that threat modeling brings ensures a more efficient deployment of security measures, thereby enhancing the resilience of the entire network against sophisticated cyber-attacks.
Resource Allocation in Threat Prevention
The efficient allocation of resources to threat prevention forms the backbone of a strong defense strategy. When organizations channel their resources towards recognized and likely threats, they create a robust shield that ensures comprehensive security coverage. This involves prioritizing the allocation based on a rigorous risk assessment and leveraging threat intelligence that highlights the specific threats your network might face. Such strategic allocation ensures that high-risk areas receive the attention they require, effectively neutralizing potential threats before they can inflict damage.
One practical implication of resource allocation in threat prevention includes adopting advanced security technologies like intrusion detection systems (IDS) and intrusion prevention systems (IPS). These tools, coupled with human intelligence and swift response protocols, form a dynamic defense mechanism capable of responding to both known and unknown threats. By focusing on recognized threats and employing a layered security approach that includes both technical solutions and trained security personnel, organizations can create a resilient defense matrix.
Implementing Access Controls
Principle of Least Privilege
Central to securing networks is the principle of ‘least privilege,’ which mandates that users and systems should have the bare minimum access necessary to perform their functions. By limiting permissions, the range of damage from potential breaches is reduced. Implementing this principle involves not only setting strict access controls but also regularly auditing these permissions to ensure they remain appropriate. This proactive stance significantly reduces the attack surface within the network, as even if one part is compromised, the intruder’s reach is restricted.
Moreover, the principle of least privilege extends beyond just user access. Systems and applications should also operate with minimal privileges. When an application or process only has access to what it absolutely needs, it curtails the potential pathways an attacker can exploit. Embedding this principle into the very policy fabric of the organization tightens security, ensuring that every entity within the network only interacts with its minimum required components.
Robust Authentication Methods
To fortify access control, robust authentication methods are indispensable. Secure devices and strong authentication policies act as the first line of defense. Multi-factor authentication (MFA), for example, provides an added layer of security beyond simple password-protected access. Authentication methods should be continuously assessed for integrity and updated to counteract evolving threats. Machines, systems, and users alike should undergo rigorous identity verification processes.
In addition to conventional practices, leveraging biometric data and cryptographic tokens can provide higher assurance in authentication. Conducting regular penetration tests helps in identifying any weaknesses in the current authentication systems. Furthermore, it’s imperative for organizations to employ proper systems administration architectures that support secure and efficient identity management. Authentication should not be a one-time procedure but an ongoing process that adapts to new threats perpetually.
Securing Administrative Access
Risks of Privileged Accounts
Privileged accounts carry significant risks as they hold the potential to make sweeping changes within a network. These accounts are often the prime targets for attackers, given their extensive access rights. Breaches involving privileged accounts can lead to devastating consequences, making it imperative for organizations to secure these accounts with utmost diligence. Failure to protect administrative access could result in unauthorized control over critical systems, leading to potential data breaches, service disruptions, and financial losses.
The elevated risk associated with these accounts stems from their ability to override standard security controls. When compromised, an attacker could escalate their privileges further, gain administrator-level control, and carry out actions undetected. Hence, ensuring that these accounts are robustly protected with stringent policies and security measures is crucial. Regular monitoring and auditing of privileged access activities are also essential to detect any suspicious behavior promptly.
Strategies for Securing Administrative Access
Implementing effective strategies to secure administrative access begins with enforcing strict access policies and adopting the principle of least privilege. Only those who absolutely need administrative access should possess it, and their activities should be closely monitored. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a fundamental requirement for accessing these privileged accounts. Furthermore, tools such as privileged access management (PAM) solutions offer additional layers of security by controlling and managing privileged account access through automated policies.
In addition to these technical measures, a cultural shift towards security awareness is necessary. Administrators should undergo regular training to recognize phishing attempts and other social engineering tactics that could potentially compromise privileged accounts. Incorporating regular audits and reviews of administrative access helps in identifying any anomalies and enforcing compliance with security policies. By combining technological solutions with behavioral vigilance, organizations can substantially reduce the risks associated with privileged accounts.
Enhancing Authentication with Passwords and PINs
In today’s digital age, enhancing authentication methods is crucial for ensuring security. Passwords and PINs (Personal Identification Numbers) are foundational elements in many authentication systems. They offer a basic yet effective layer of security by requiring users to provide a secret credential that verifies their identity. Combining strong, unique passwords with additional factors like biometric verification or multi-factor authentication (MFA) further enhances protection against unauthorized access and cyber threats. Utilizing a combination of these methods can significantly reduce the risk of security breaches and improve overall data integrity.
Importance of Multi-Factor Authentication
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is crucial in enhancing the security of online accounts. By requiring multiple forms of verification, it adds an extra layer of protection that makes it more difficult for unauthorized users to gain access. This method ensures that even if one factor, like a password, is compromised, additional barriers are in place to safeguard sensitive information.
While passwords and PINs remain fundamental for user authentication, the increasing sophistication of cyber-attacks necessitates the use of multi-factor authentication (MFA). Relying solely on single authentication factors, such as passwords, exposes networks to significant risks, including phishing attacks and credential theft. MFA enhances security by requiring users to provide additional verification factors, typically something they know (password), something they have (security token), and something they are (biometric verification). This layered approach ensures a more robust defense against unauthorized access.
Integrating MFA into the network security framework should be a priority. Implementing it can significantly reduce the likelihood of successful attacks, even if passwords are compromised. For example, an attacker might gain access to a password but would still be thwarted by the need to provide a second or third verification factor. With the rise in remote work and the growing use of cloud services, MFA provides an essential layer of protection in diverse and decentralized network environments.
Strong Password Management
Effective password management is crucial for bolstering network security. Strong, unique passwords for each account reduce the risk of unauthorized access. Password policies should enforce complexity requirements, such as a combination of letters, numbers, and special characters, to make passwords more resilient against brute force attacks. Additionally, regular password expiration policies encourage users to update their credentials periodically, minimizing the risk of long-term vulnerabilities.
Organizations can employ password managers to help users generate and store complex passwords securely. These tools can also autofill passwords and alert users if they are reusing passwords across different sites, further enhancing security. Educating employees about the dangers of phishing and social engineering attacks and training them to recognize these threats are vital components of a comprehensive password management strategy. Overall, fostering a culture of diligent password practices contributes significantly to safeguarding network integrity.
Utilizing Allow Lists and Deny Lists
Functionality of Allow and Deny Lists
Allow and deny lists are essential tools in access control, serving as gatekeepers to protect network resources. Allow lists, which permit access to specific approved entities, are generally preferred for enhanced security. By restricting access to only verified and trusted resources, allow lists adhere to the principle of least privilege, minimizing potential attack vectors. This controlled approach ensures that only authorized users, applications, or IP addresses can connect with the network, creating a fortified defense mechanism.
Deny lists, on the other hand, work by blocking access to known malicious or unauthorized entities. While this method is useful, it is inherently reactive and can be less effective against new or unknown threats. Deny lists require constant updates to remain effective, as emerging threats can exploit any gaps. However, combining both allow and deny lists can present a holistic security approach, ensuring that only trusted sources are granted access while actively blocking harmful or unrecognized entities.
Limitations of Deny Lists
Despite their utility, deny lists have certain limitations that can impact overall security effectiveness. Since deny lists are inherently reactive, they can only protect against previously identified threats. This creates a reliance on timely threat intelligence and regular updates to maintain effectiveness. Any delay in updating the deny list can leave the network vulnerable to new strains of malware or novel attack methods. Additionally, false positives, where legitimate traffic is misclassified as malicious, can disrupt normal operations and impede productivity.
Moreover, overly extensive deny lists can become cumbersome to manage, particularly in large organizations with complex network environments. The process of maintaining and updating these lists can be resource-intensive, necessitating dedicated personnel and sophisticated threat intelligence systems. In contrast, allow lists present a more streamlined and proactive security approach, ensuring that only pre-approved and verified entities gain network access. By focusing on a combination of both approaches, organizations can craft a balanced and effective security strategy.
Leveraging Certificates for Authentication
Robustness of Certificates
Certificates offer a robust and highly secure method of authentication compared to traditional mechanisms like passwords. Digital certificates employ cryptographic techniques to validate the identity of devices, users, and applications, ensuring secure communication channels within the network. The complexity of breaking cryptographic keys makes certificates a reliable and resilient option against various cyber threats. Although implementing and maintaining a certificate-based authentication system can be challenging, the security benefits far outweigh the initial complexities.
Certificates are widely used in securing network access, Transport Layer Security (TLS) for encrypting web traffic, and Virtual Private Networks (VPNs). For instance, TLS/SSL certificates encrypt data transmitted between a user’s browser and a web server, ensuring confidentiality and integrity. Similarly, VPNs leverage certificates to establish secure tunnels over untrusted networks, protecting data in transit. By incorporating certificate-based authentication, organizations can greatly enhance the trustworthiness and reliability of their network communications.
Use Cases for Certificates
The application of certificates in network security extends beyond simple authentication, covering various critical scenarios. For example, certificates can be instrumental in securing email communications through protocols like Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (S/MIME), which ensures that email content is encrypted and digitally signed. This prevents unauthorized access and verifies the sender’s identity. Certificates also play a crucial role in securing Internet of Things (IoT) devices, where mutual authentication between devices and networks is vital to protect against unauthorized access and data breaches.
Moreover, certificates facilitate the implementation of secure application architectures, including server-to-server communications and client-server authentications. They enable encrypted communication channels, ensuring data exchanged between systems remains confidential and tamper-proof. By leveraging certificates effectively, organizations can not only secure their network infrastructure but also foster greater confidence in digital interactions both internally and externally. This widespread application of certificates underscores their importance in a comprehensive network security strategy.
Designing Secure Network Architecture
Importance of Security in Network Design
Embedding security into the design phase of network architecture is pivotal in mitigating potential risks and reducing the impact of compromises. A well-thought-out security-focused network design acts as the first line of defense against cyber threats. By incorporating principles such as defense-in-depth and least privilege from the outset, organizations can create a resilient network infrastructure that withstands various attack vectors. This approach ensures that security considerations are not an afterthought but an integral part of the network design process.
Key elements of secure network design include segmenting networks, implementing robust access controls, and ensuring redundancy to mitigate single points of failure. By dividing the network into smaller segments or zones, organizations can limit the lateral movement of attackers and protect critical systems and data. Additionally, incorporating advanced security measures like firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS), and secure gateways enhances the overall network security posture. These measures collectively ensure that the network is designed to prevent, detect, and respond to threats effectively.
Facilitating Detection of Malicious Activity
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, facilitating the detection of malicious activity requires constant vigilance and adaptation. Security professionals must continuously update their methodologies and tools to stay ahead of cyber threats. This includes leveraging advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, to analyze patterns and identify potential vulnerabilities before they can be exploited by malicious actors. Through proactive monitoring and swift response strategies, organizations can mitigate risks and protect their sensitive information from increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks.
A well-designed network architecture not only prevents unauthorized access but also facilitates the detection and response to malicious activities. Proactive monitoring and logging mechanisms are essential components that help in identifying suspicious behavior and potential breaches. By implementing centralized logging and monitoring systems, organizations can gain real-time visibility into network activities, enabling quick detection and response to threats. These systems can analyze patterns and alert security teams to anomalies that may indicate a compromise.
Moreover, incorporating network segmentation and access controls helps isolate and contain malicious activities, preventing them from spreading across the network. Techniques like micro-segmentation further enhance security by creating smaller, more manageable segments within the network that can be closely monitored and controlled. Combined with advanced analytics and threat intelligence, these measures enable organizations to detect threats early and take swift remedial actions, thereby minimizing potential damage and ensuring a resilient network environment.
Implementing Network Segmentation
Network segmentation involves dividing a computer network into smaller, manageable segments to enhance performance, improve security, and simplify compliance. By isolating critical systems and sensitive data, organizations can minimize the impact of potential breaches and limit the lateral movement of threats. This approach not only protects sensitive information but also helps in meeting regulatory requirements more effectively.
Benefits of Network Segmentation
Network segmentation plays a crucial role in enhancing overall security by dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments. This approach allows for better control of traffic flow and access between different segments, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and improving the network’s security posture. By segmenting the network, organizations can limit the lateral movement of attackers, making it more challenging for them to spread and access critical systems. Each segment can be tailored with specific security controls and policies relevant to the assets it contains.
Additionally, network segmentation provides the ability to enforce stricter access controls and monitoring for sensitive areas of the network. For instance, critical financial systems or customer databases can be isolated in secure segments with enhanced security measures, ensuring that only authorized personnel can access these resources. In the event of a breach, segmentation helps contain the attack within a single segment, preventing the attacker from moving freely across the entire network. This containment strategy is vital for minimizing the impact and facilitating effective incident response.
Protecting Management Interfaces
One of the key benefits of network segmentation is the ability to protect management interfaces used by administrators to configure and manage the network infrastructure. Management interfaces are often targeted by attackers due to the elevated privileges they hold. By isolating these interfaces in separate, secure segments, organizations can implement additional security controls, such as restricted access, multi-factor authentication, and continuous monitoring to safeguard them against unauthorized access and attacks.
Moreover, securing management interfaces within dedicated segments ensures that only trusted and authenticated devices have access, reducing the risk of exploitation through compromised endpoints. Implementing strong encryption for management traffic and regularly auditing access logs can further enhance the security of these interfaces. By adopting a segmented approach to network design, organizations can create fortified zones that protect critical management functions and maintain the integrity and stability of the overall network.
Adopting Zero Trust Architecture
Concept of Zero Trust
The concept of Zero Trust architecture revolutionizes traditional network security by eliminating the notion of inherent trust within the network. Under Zero Trust, every access request is subject to strict verification, regardless of the requestor’s location within or outside the network perimeter. This approach mandates continuous authentication, authorization, and validation of users, devices, and applications based on defined security policies. By adopting Zero Trust principles, organizations can create a more secure and resilient network environment that is less susceptible to breaches.
Zero Trust operates on the principle of ‘never trust, always verify,’ ensuring that all access requests are thoroughly vetted before granting permission. This model requires a combination of strong identity and access management (IAM), micro-segmentation, and real-time threat detection to enforce stringent security controls. Implementing Zero Trust not only protects against external threats but also mitigates risks from insider threats by restricting access based on the least privilege principle and continuously monitoring all activities.
Building Context for Security
One of the core elements of Zero Trust architecture is building context for security by leveraging multiple factors such as strong authentication, authorization, device health, and data value. By gathering and analyzing contextual information, organizations can make informed decisions about granting or denying access requests. For instance, authentication can be based on user identities, multi-factor authentication, and device compliance with security policies. This multi-layered approach ensures that access is granted only to verified and trusted entities.
Authorization within a Zero Trust model involves dynamic policies that consider user roles, behaviors, and the sensitivity of the requested data or resources. Continuous monitoring of user activities and device health helps detect anomalies and potential threats in real-time, allowing for immediate response actions. By building a comprehensive security context, organizations can enhance their threat detection capabilities, prevent unauthorized access, and maintain a robust security posture that adapts to evolving threat landscapes.
Protecting Data in Transit
Importance of Data Protection
Protecting data as it moves across the network is crucial for maintaining its confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Data in transit is particularly vulnerable to interception and unauthorized access, making encryption an essential measure to safeguard sensitive information. Employing secure communication protocols such as TLS (Transport Layer Security) ensures that data transmitted over the network is encrypted and secure from eavesdropping and tampering. This is especially important for protecting data traversing between different network segments, devices, and external networks.
Ensuring data protection in transit also involves securing communication channels within the organization’s intranet and between endpoints. This can be achieved through the use of Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), which create secure, encrypted tunnels over untrusted networks, protecting data from potential threats. Regularly updating and maintaining encryption protocols helps address vulnerabilities and prevents attackers from exploiting weaknesses in outdated systems. By prioritizing data protection in transit, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and secure their communication channels.
Role of VPNs
Emerging cyber threats significantly jeopardize network security, making it imperative for organizations to implement strong security strategies. The swift evolution of cyber-attacks necessitates a proactive stance in securing and managing networks. In response, this article offers a comprehensive guide on effectively mitigating these advancing threats.
It delves into various facets of network security, presenting essential insights that can help organizations stay a step ahead of cybercriminals. By adopting cutting-edge technologies and best practices, such as real-time threat detection, consistent software updates, and employee training, businesses can reinforce their defenses against attacks.
Advanced measures like multi-factor authentication (MFA), endpoint protection, and intrusion detection systems (IDS) are crucial in creating a robust security framework. Moreover, the article emphasizes the importance of continuous monitoring and rapid response protocols to swiftly address any vulnerabilities that may arise.
Furthermore, collaboration and sharing of threat intelligence between organizations can aid in combating these threats more effectively. Staying informed about the latest cybersecurity trends and updates is also essential for maintaining network integrity. By following these comprehensive guidelines, organizations can better safeguard their networks from the ever-growing landscape of cyber threats.